Download the database (.xls) – Download the entire Chartbook (.pdf)
Sources and References
Sources:
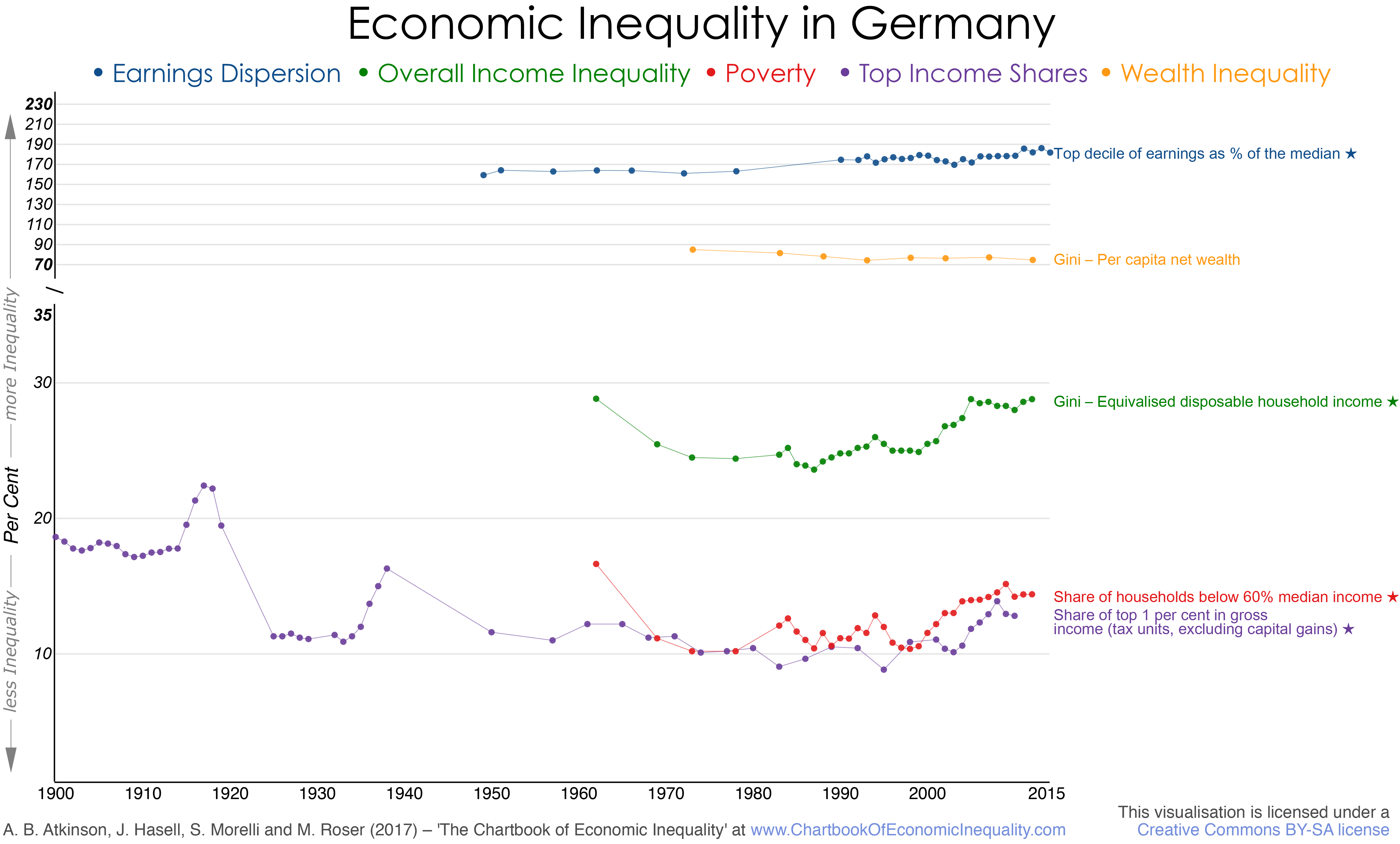
Overall inequality: Gini coefficient of equivalised (modified OECD scale) disposable household income for all persons in private households for all Germany (West Germany from 1984 to 1990) from SOEPmonitor 1984-2013, SOEP Survey Paper 284, page 83, note that the data are based on information collected in the German Socio-Economic Panel on annual income (preceding year, so that the 2012 data are from the 2013 survey), linked backwards at 1983 to data from the EVS (Income and Expenditure Survey) for West Germany from Becker (1997, Tabelle 1) and Hauser and Becker (2001, page 89).
Top income shares: Share of top 1 per cent in total gross income (tax units, excluding capital gains) from WID.world, covering West Germany from 1950 to 1990 and thereafter unified Germany; earlier series covering Prussia before 1919 and the German Reich from 1925 to 1938 (including capital gains), based on the work of Dell (2007) and Bartels and Jenderny (2015).
Poverty measures: Percentage of individuals in households with equivalised (modified OECD scale) disposable income below 60 per cent of the median for all persons in private households for all Germany (West Germany from 1984 to 1990) from SOEP Group (2015), SOEP2013-SOEPmonitor 1984-2013, SOEP Survey Paper 284, page 91, FGT=0 column (e.g. when Foster–Greer–Thorbecke poverty index reduces to the headcount ratio) – note that the data are based on information collected in the German Socio-Economic Panel on annual income (preceding year, so that the 2012 data are from the 2013 survey)-; linked at 1983 to series for percentage of individuals in households with equivalised (original OECD scale) disposable household income below 50 per cent of the mean for all persons of German nationality in private households for West Germany, from Becker (1997, Tabelle 2).
Dispersion of earnings: Earnings at top decile as percentage of median earnings, from OECD iLibrary, Employment and Labour Market Statistics, Gross earnings decile ratios (accessed 22 February 2017), linked (via 1995) to earlier series covering West Germany from 1949 to 1991 and Germany till 1995 from Atkinson (2008, Appendix H, Table H.4).
Wealth inequality: Gini coefficient per-capita net wealth covering Germany taken from Frick, Grabka and Hauser (2010, Tabelle 2.6), using SOEP data – updated figures for 2002, 2007, and 2012 provided by Markus Grabka; linked at 2002 on the assumption of no change to 2003 using the earlier series based on the income and expenditure survey – EVS; further linked at 1998 to earlier EVS 1973-1993 series related to West Germany.
References:
- Atkinson, A B, 2008, The changing distribution of earnings in OECD countries, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- Bartels, C, and Jenderny, K, 2015, „The Role of Capital Income for Top Income Shares in Germany”, WTID Working paper, 2015/1.
- Becker, I, 1997, “Die Entwicklung der Einkommensverteilung und der Einkommensarmut in den alten Bundesländern von 1962 bis 1988” in I Becker and R Hauser, editors, Einkommensverteilung und Armut , Campus, Frankfurt.
- Dell, F, 2007, “Top incomes in Germany throughout the twentieth century: 1891-1998” in A B Atkinson and T Piketty, editors, Top incomes over the twentieth century, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- DIW (Deutsche Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung), 1973, “Einkommensverteilung und –schichtung der privaten Haushalte in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland 1950 bis 1970”, Wochenbericht, No 25, Berlin.
- Frick, J R, Grabka, M M and Hauser, R, 2010, Die Verteilung der Vermögen in Deutschland, Edition Sigma, Berlin.
- Hauser, R and Becker, I, 2001, Einkommensverteilung im Querschnitt und im Zeitverlauf 1973-1998, Bundesministerium für Arbeit und Sozialordnung, Bonn.
- SOEP Group, 2015, SOEP2013-SOEPmonitor 1984-2013, SOEP Survey Paper 284: Series E. Berlin: DIW/SOEP



